1. What is a CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Grating
CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten alloy grating is an anti-scattering device used in X-ray imaging systems, mainly made from tungsten, nickel, iron, or copper. It improves image contrast and clarity by shielding scattered radiation while allowing primary X-rays to pass through, and is widely used in medical and industrial fields.
CTIA GROUP LTD and its parent company CTIA GROUP LTD have been deeply engaged in the tungsten-molybdenum products industry for nearly 30 years, specializing in flexible customization and global services for tungsten-molybdenum products, capable of custom processing various specifications, performance, sizes, and grades of tungsten-molybdenum products according to customer needs. For more information on tungsten alloys, please visit the website: http://www.tungsten-alloy.com/index.htm. For any tungsten alloy grating products, please contact CTIA GROUP LTD: sales@chinatungsten.com, 0592-5129595.

2. Working Principle of CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Gratings
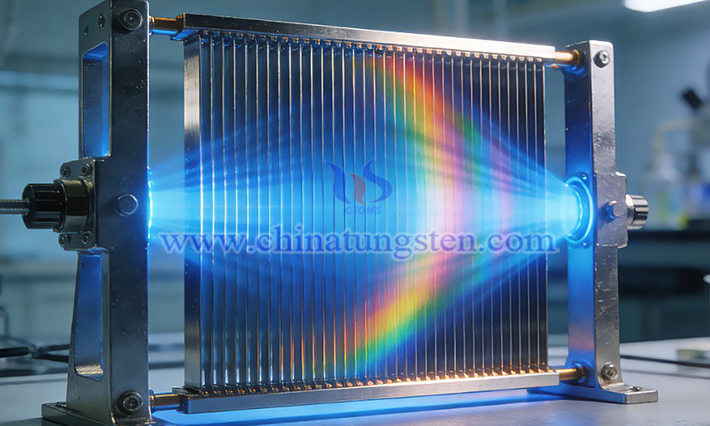
The working principle of tungsten alloy gratings is based on the selective absorption of X-rays. The grating consists of parallel arranged thin tungsten alloy strips, with low-attenuation materials such as carbon fiber or aluminum filled in the gaps. Primary X-rays (parallel to the grating strips) pass directly through the gaps to the detector, while scattered X-rays (deviated direction) are absorbed by the tungsten alloy thin strips, because tungsten's high atomic number and high density give tungsten alloy a high absorption rate for X-rays.
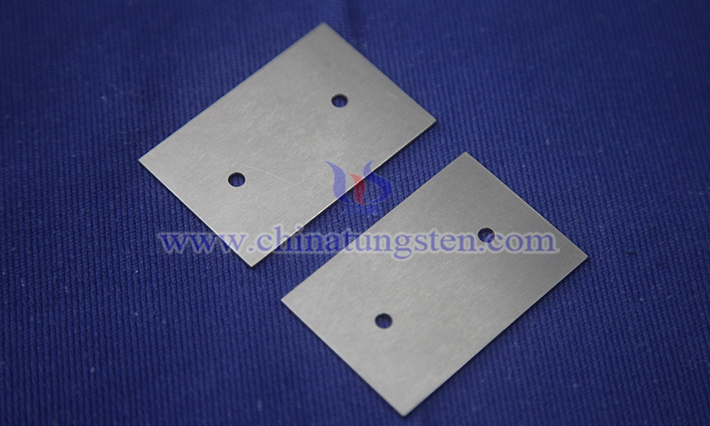
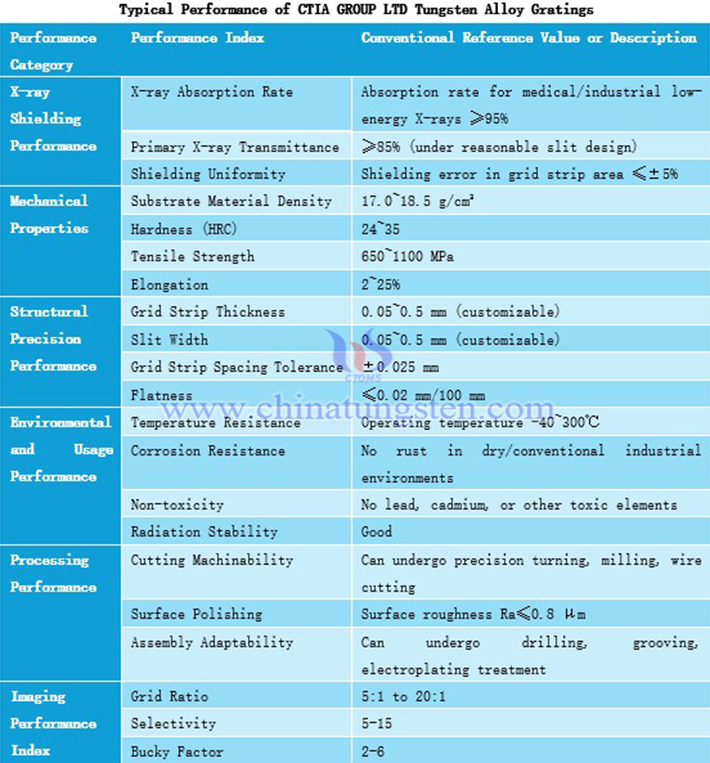
3. Typical Performance of CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Gratings
The main advantage of CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten alloy gratings lies in their excellent X-ray shielding capability, which can efficiently absorb scattered radiation while maintaining high transmittance of primary rays, achieving a good balance between scattering suppression and imaging flux. In addition, tungsten alloy gratings also have high density, high hardness, excellent tensile strength, and certain plasticity, enabling the gratings to achieve miniaturization and thin design while exhibiting outstanding resistance to deformation, scratch resistance, and long-term structural stability, far superior to traditional lead-based or iron-based gratings.
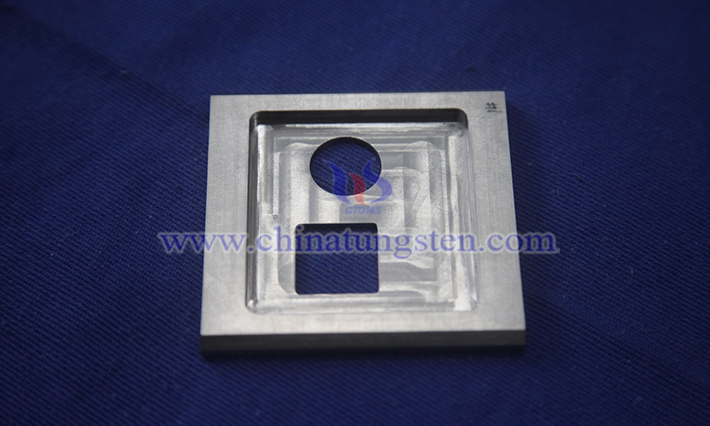
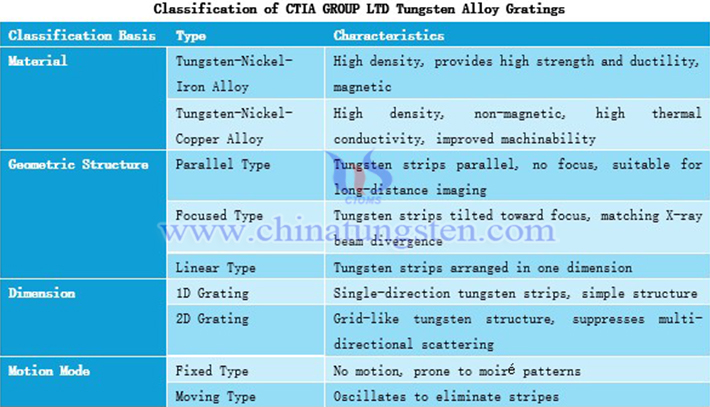
4. Classification of CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Gratings
According to differences in material, geometric structure, dimension, or motion mode, CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten alloy gratings can be divided into many types. Geometric structure classification emphasizes the matching between the grating and the X-ray source, with focused type more common in medical applications to reduce edge distortion. Dimension classification highlights the advantages of 2D gratings, which are superior to 1D type in multi-directional scattering suppression, especially in cone-beam CT to improve image uniformity. Motion mode balances image quality and artifact risk, with moving type preferred in clinical use to avoid visible stripes.
5. Production Methods of CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Gratings
The production of tungsten alloy gratings mainly adopts powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing technologies. Powder metallurgy for preparing tungsten alloy gratings: mix tungsten powder with nickel, iron, and other binders, press and form, sinter in hydrogen atmosphere, and finally precision roll or cut into thin strips. Traditional assembly methods include alternately laminating tungsten alloy strips with carbon fiber spacer layers and bonding with adhesive. Laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing technology can be used to prepare 2D tungsten alloy gratings: using pre-mixed tungsten powder, nickel powder, and iron powder as raw materials, through layer-by-layer selective laser melting to directly form complex grid structures.
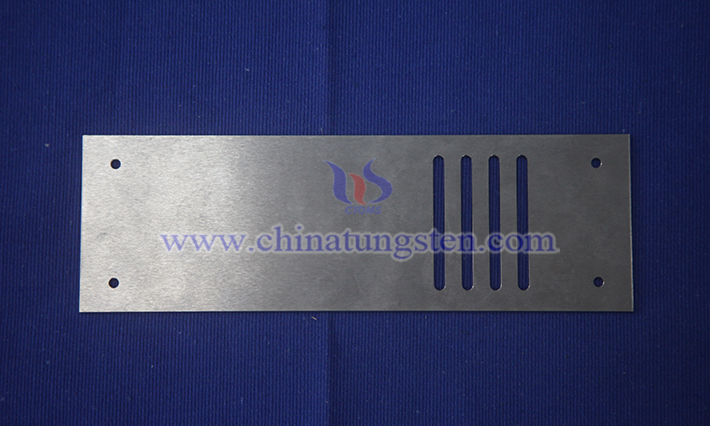

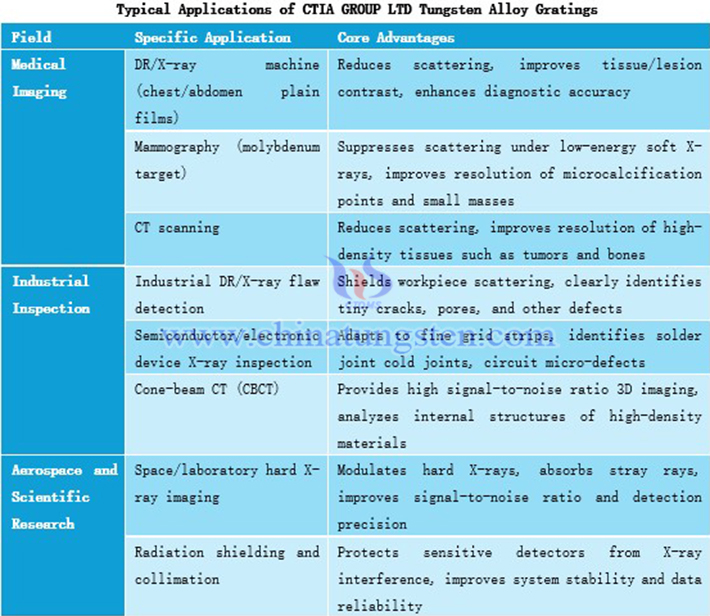
6. Applications of CTIA GROUP LTD Tungsten Alloy Gratings
The applications of CTIA GROUP LTD tungsten alloy gratings are mainly distributed in medical imaging, industrial inspection, aerospace, and scientific research fields. In medical imaging, it is widely used in conventional DR/X-ray machines (chest and abdomen plain films), mammography (molybdenum target), and CT scanning. By efficiently absorbing scattered radiation, it significantly reduces image haze, improves tissue boundaries, lesion contrast, microcalcification points, and resolution of small masses, especially achieving a balance between scattering suppression and low-dose imaging under low-energy soft X-rays, improving diagnostic accuracy and optimizing patient radiation protection. In industrial inspection, it is mainly applied in industrial DR/X-ray flaw detection (alloys/composites), semiconductor/electronic device inspection, and cone-beam CT. Tungsten alloy gratings shield workpiece scattered rays, clearly identify tiny defects, support high-precision nondestructive testing (NDT), and adapt to fine grid strip design to meet the strict quality requirements of precision electronic components. In aerospace and scientific research, it is applied in space/laboratory hard X-ray imaging (such as astronomical observation, high-energy physics detection). By modulating directed hard X-ray beams and absorbing stray rays, it improves imaging signal-to-noise ratio and detector precision, while providing reliable radiation shielding.